Phénomènes de Transport Thermique
MEMBRES DE L'EQUIPE
Mathieu Bardoux (MCF)
Sylvain Delenclos (MCF)
Michael Depriester (PR) (Page personnelle)
Fabrice Goutier (MCF)
Abdelhak Hadj Sahraoui (PR)
Stéphane Longuemart (PR) (responsable d’équipe)
Suhao Wang (PR Jr) (Page personnelle)
Doctorants
Thèses en cours
| Karthika PAIRADUKHAM | 2025-2027 | Synthesizing novel conjugated polymers for organic thermoelectrics |
| Tian Qingyu | Depuis 2020 | Modélisation, élaboration et caractérisation expérimentale de la conductivité thermique de superréseaux de type oxydes |
| Nouha Drame | Depuis 2021 | Development of a device for measuring the conversion of heat into electricity and the realization of a thermoelectric generator |
| Mamadou Barry | Depuis 2022 | Synthèse et caractérisation de nouveaux dérivés de MXèmes pour le stockage et la conversion énergétique |
Thèses soutenues
Post-doctorants
- Atul Tripathi (2021).
- Dharmendra Singh (2018).
- Jan Leys, contrat post-doctoral de l’ULCO. Calorimétrie et mesure de l’effet électrocalorique (2015).
Professeurs Invités
Eliane BSAIBESS
Assistant professor
Sciences and Engineering Department, Sorbonne University of Abu DhabiGeorgios Kordogiannis
Research Associate
Condensed Matter Physics Department, Jožef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia.Abdelkrim MAAROUFI
Professeur
Université Mohammed V, Faculté des Sciences,
Département de Chimie,
Laboratoire des Matériaux Composites, Polymères et Environnement (LMCPE)- Kordogiannis Georgios, Jozef Stefan Institute, université d’Athènes (2022).
- Mihaela Streza, Université de Cluj Roumanie (2019).
- Dorin Dadarlat, NIRDIMT, Cluj-Napoca, Roumanie (2018).
- Ziad Herro, Université Libanaise, Beyrouth (2018).
- Christ Glorieux, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgique (2016).
- Dorin Dadarlat, NIRDIMT, Cluj-Napoca, Roumanie (Juin-Juillet 2015).
Les mécanismes de transport thermique jouent un rôle important dans le développement de dispositifs techniques afin d’en accroître leur performance et leur fiabilité. Selon les applications, on cherchera à augmenter ou à diminuer la conduction thermique. Par exemple, concernant les matériaux thermoélectriques, l’efficacité de conversion de la chaleur en électricité est améliorée lorsque la conductivité thermique est minimisée. Inversement, d’autres procédés de conversion de l’énergie comme les échangeurs de chaleur, le stockage de l’hydrogène nécessitent
une conductivité thermique élevée. Le « réglage » des paramètres thermiques implique de bien comprendre les processus thermophysiques se déroulant au sein des matériaux. Le transport thermique peut ainsi être modifié par la création d’interfaces, de défauts, par nanostructuration, par ajout d’inclusions ou encore par confinement spatial. L’étude des effets thermiques associés aux transitions structurales est également importante comme par exemple dans les matériaux à changement de phase pour stocker la chaleur, les mémoires à changement de phase pour densifier la quantité de données stockées, dans la conservation des
tissus biologiques ou encore dans les dispositifs à cristaux liquides pour réduire leur temps de réponse et la valeur des champs électriques nécessaires. La compréhension au niveau fondamental des mécanismes physiques survenant aux différentes échelles est nécessaire afin de pouvoir par la suite optimiser les dispositifs précédemment mentionnés.
Pour l’étude de ces mécanismes, l’UDSMM a développé des techniques de caractérisation photothermiques (photopyroélectricité, photothermoélectricité, radiométrie infrarouge, détection photoacoustique…), domaine dans lequel le laboratoire est internationalement reconnu. L’expertise acquise par notre laboratoire a permis de contribuer au développement dans différents domaines dont le détail est donné ci-dessous.
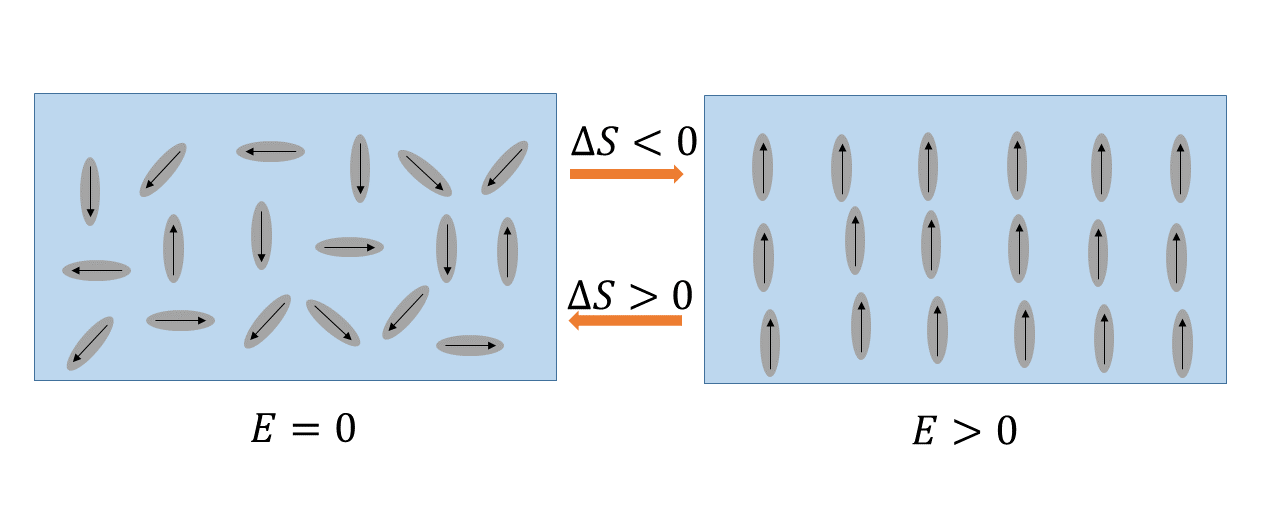
L’effet électrocalorique (EC) correspond à la variation de température réversible d’un matériau polaire sous l’effet d’un champ électrique. Ce phénomène a connu un regain d’intérêt suite à la découverte d’un effet électrocalorique « géant » dans des films ferroélectriques, permettant d’envisager son application pour la réalisation de dispositif réfrigérant performant, à l’instar de l’effet magnétocalorique. La caractérisation de cet effet consiste en la mesure de de la variation de la température et du flux de chaleur échangé suite à la l’application d’un champ électrique au matériau.
Dans le cadre des activités de l’équipe et à travers la préparation de différentes thèses en cours ou déjà soutenues, nous nous intéressons aux propriétés électrocalorique de différents matériaux ferroélectriques solides, liquides ou cristaux liquides. L’objectif est d’élaborer de nouveaux matériaux présentant des performances EC qui permettent leur utilisation dans dispositifs de réfrigération.
Ainsi, différents matériaux ferroélectriques sont élaborés et caractérisés en utilisant différentes techniques dont certaines développées et mises au point au laboratoire. A titre d’exemple, des études sont (ou ont été) réalisés sur des matériaux tels que :
- Des cristaux liquides (FELIX-017/000 et le OB4HOB) dans leur phase ferroélectrique
- Le Titanate de baryum dopé au samarium synthétisé par voie solide-solide ou sol-gel sous forme de pastilles ou de films minces
- Des polymères ferroélectriques en couches minces à base de poly(fluorure de vinylidène-trifluoroéthylène) (PVDF TrFe)
Notre équipe a acquis une bonne expertise dans la caractérisation thermique et électrique des matériaux ferroélectriques. Cela nous a permis de mettre au point plusieurs techniques originales de caractérisation électrocalorique directes ou indirectes. La première, directe, permet la mesure de la variation de température et du flux de chaleur à l’aide d’un calorimètre adiabatique. Une deuxième technique, photothermique, appelée thermoréflectance, permet de mesurer la température de surface de l’échantillons à l’aide d’un faisceau sonde se réfléchissant sur celle-ci. Une autre technique indirecte exploite le signal photopyroélectrique obtenu lorsque le matériau électrocalorique est éclairé par un faisceau lumineux d’intensité modulée
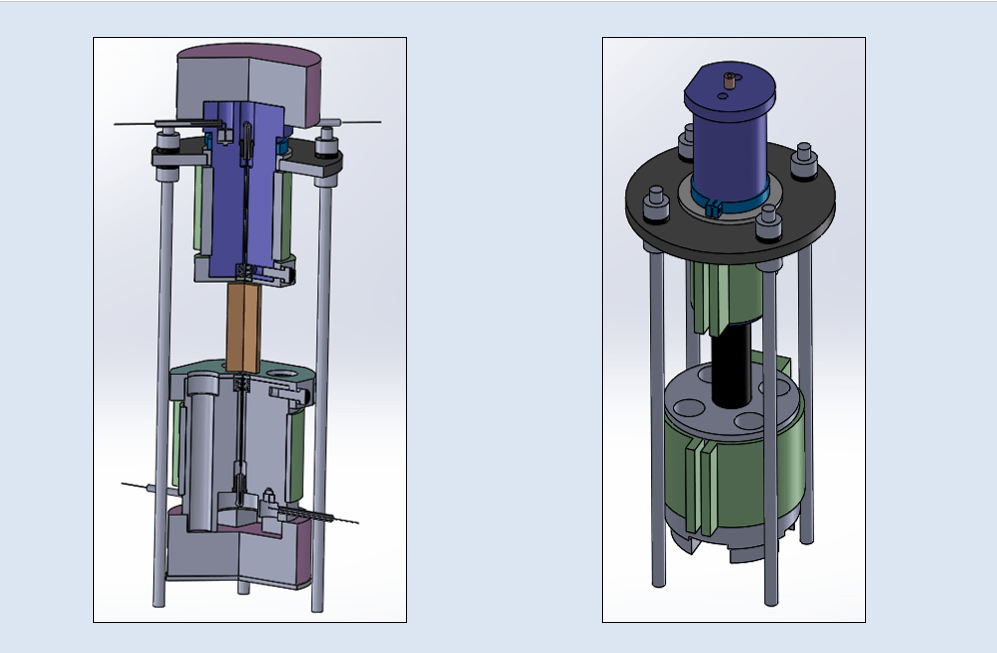
Par ailleurs, un démonstrateur de réfrigération électrocalorique a été mis au point, les premiers résultats obtenus ont permis d’évaluer et de discuter les différentes solutions techniques proposées. Nous avons ainsi pu montrer la faisabilité de l’utilisation de l’effet électrocalorique pour la réfrigération, validant ainsi l’idée de l’exploitation de l’effet électrocalorique comme une solution alternative aux techniques usuelles de réfrigération. De par sa conception, ce démonstrateur peut être envisagé comme un banc d’essai permettant l’optimisation des propriétés des matériaux et des processus associés dans le cadre d’une application de l’effet électrocalorique pour la réfrigération.
> ancien texte<<
Les matériaux dits « intelligents » ou « adaptatifs » sont des systèmes capables de modifier leurs propriétés physiques en réaction à des sollicitations extérieures (champ électrique ou magnétique, flux lumineux, contrainte,…). C’est le cas des cristaux liquides (CL) connus comme étant des matériaux dont les propriétés optiques (biréfringence, rotation de l’axe optique) sont stimulables par un champ électrique modeste (~1V/mm). L’une des applications qui en découle est leur utilisation dans des dispositifs d’affichage ou comme modulateurs électro-optiques.
Beaucoup d’efforts portent actuellement sur l’étude de CL de type nématique dopés par des dispersions de nanoparticules isolantes ou conductrices, afin d’améliorer leurs propriétés (amplification des réponses électro-optiques des CL dopés et abaissement des champs seuils électrique ou magnétique (transition de Fredericks)). Le milieu cristal liquide induit des interactions, souvent de nature élastique, entre les nano-objets dispersés permettant ainsi leur auto-organisation sous forme de structures inédites (chapelets, strates,…) selon leurs formes (sphériques ou bâtonnets), soulignant ainsi la corrélation entre les particules dopantes et le milieu hôte.
Depuis quelques années, nous nous intéressons à des systèmes colloïdaux constitués de dispersions de nanoparticules solides, ferroélectriques ou semi-conductrices, dans un milieu cristal liquide à molécules polaires ou ferroélectriques. L’objectif fondamental est d’appréhender les interactions de nature électrique (en plus de celles élastiques) entre le milieu CL (du fait que les molécules du CL portent spontanément un dipôle électrique ou une polarisation dans le cas d’un ordre ferroélectrique) et les nanoparticules. Expérimentalement, il s’agit de mesurer l’impact de ces nanoparticules dispersées sur les propriétés diélectriques, optiques et ferroélectriques de ces matériaux
L’effet électrocalorique (electrocaloric effect : ECE) correspond à la variation de température réversible d’un matériau polaire sous l’effet d’un champ électrique. Ce phénomène a connu un regain d’intérêt suite à la découverte d’un effet électrocalorique « géant » dans des films ferroélectriques, permettant d’envisager son application pour la réalisation de dispositif réfrigérant performant, à l’instar de l’effet magnétocalorique.La caractérisation de cet effet consiste en la mesure de l’évaluation de la variation de température suite à la l’application d’un champ électrique au matériau. L’UDSMM possède une bonne expertise dans la caractérisation thermique et électrique des matériaux ferroélectriques, sous forme de film minces ou de cristaux liquides par exemple. Les méthodes usuelles sont déjà disponibles au laboratoire et peuvent être complétées par des techniques plus spécifiques développées au laboratoire pour la caractérisation des propriétés thermiques de matériaux sous champ que sont les techniques photothermiques
Les matériaux thermoélectriques permettent la conversion de la chaleur en électricité sous l’effet d’un gradient de température ou de manière réciproque de transférer de l’énergie thermique dans le sens contraire au gradient de température sous l’action d’un courant électrique.
Accroitre l’efficacité de conversion des dispositifs basés sur des matériaux thermoélectriques revient à maximiser une quantité appelée figure de mérite ZT :
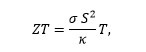
avec s, S, k et T respectivement la conductivité électrique, le coefficient Seebeck, la conductivité thermique et enfin la température du matériau considéré. Améliorer un matériau thermoélectrique revient pour une température T donnée à accroitre s et S et diminuer k. La difficulté réside à améliorer un des paramètres sans en dégrader les autres puisque ces paramètres sont inter-reliés. C’est pourquoi, en raison de la difficulté à accroitre l’efficacité de conversion, ces applications ont longtemps été cantonnées à des secteurs de niche comme le spatial où une grande fiabilité était recherchée. Ces convertisseurs suscitent depuis deux décennies un regain d’intérêt en raison de la découverte de nouvelles stratégies d’optimisation de ces matériaux basées sur les concepts d’ingénierie des bandes d’énergie et d’ingénierie des phonons, permettant ainsi de lever au moins en partie les corrélations entre paramètres.
Dans notre équipe, des matériaux thermoélectriques à base de polymères conducteurs sont élaborés. Nous développons des dispositifs basés sur ce type de matériau A titre d’exemple, nous pouvons citer le polyaniline et le poly(3,4-éthylènedioxythiophène) : poly(styrène sulfonate) de sodium (PEDOT : PSS), où des inclusions de diverses natures ont été insérées. Leurs paramètres de transport (s, S, k) sont mesurés à l’aide de techniques disponibles au laboratoire comme la spectroscopie d’impédance ou encore la technique des 4 pointes pour la conductivité électrique, un dispositif de mesure du coefficient Seebeck développé en interne. Différentes techniques originales ont-été développées au laboratoire pour déterminer la conductivité thermique. Parmi ces techniques, la radiométrie infrarouge (PTR) permet de mesurer la température d’un matériau à partir de l’émission de rayonnement infrarouge. Nous avons par ailleurs développé une technique dédiée à la caractérisation thermique des matériaux thermoélectriques appelée technique photothermoélectrique (PTE) qui consiste à exploiter la tension générée par effet Seebeck suite à la présence d’une différence de température. Cette même technique peut aussi être utilisée pour l’étude thermique de liquides mis en contact avec un matériau thermoélectrique, ce dernier servant alors de capteur.
Les recherches actuelles s’orientent vers :
- Les matériaux de type oxyde en raison de leurs relatives innocuités sur l’environnement et des performances acceptables comparées à d’autres matériaux thermoélectriques « traditionnels ».
- Les matériaux sous forme de couches minces afin de pouvoir mettre en œuvre la stratégie de minimisation de la conductivité thermique par ingénierie des phonons.
- Les inclusions de dimensions nanométriques, sous formes de quantum-dots et de structures bidimensionnelles, permettant d’explorer simultanément les concepts d’ingénierie des bandes d’énergie et d’ingénierie des phonons. Une thèse sur les MXènes est actuellement en cours sur ce thème.
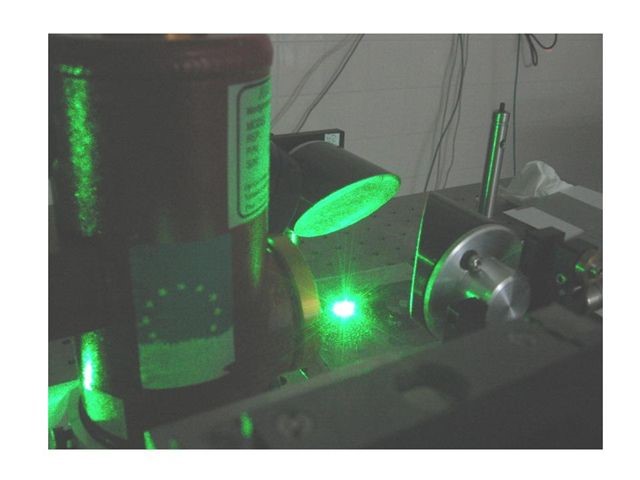
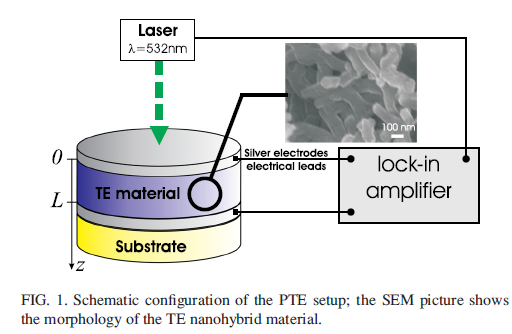
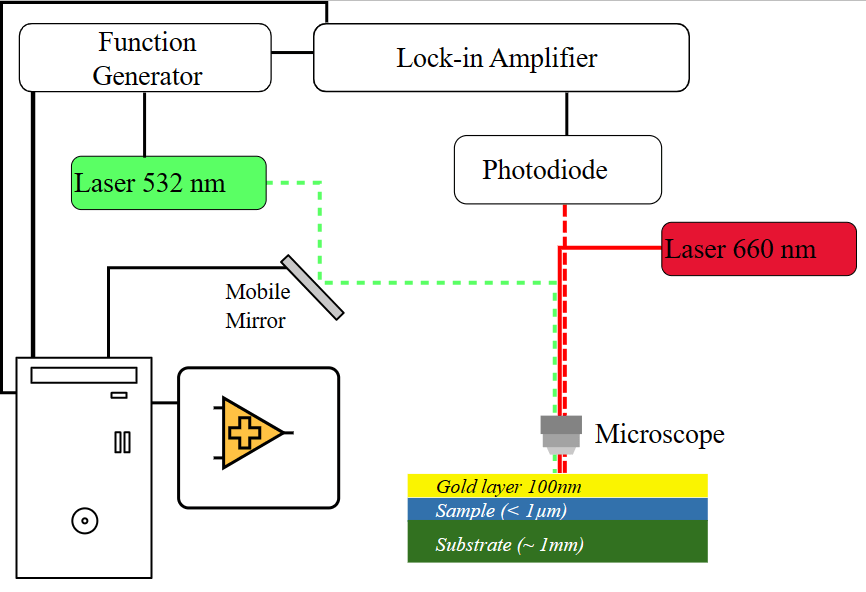
La thermoreflectance permet une mesure de température de surface sans contact, avec une résolution optique (<1µm) et une grande résolution temporelle, permettant d’étudier les transferts de chaleur au sein de couches nanométriques.
Pour ce faire, l’échantillon subit un échauffement à haute fréquence (jusqu’au MHz), soit d’origine interne (matériau électrocalorique, composant électronique en fonctionnement…) soit d’origine externe (source laser). Un laser sonde d’intensité continue se réfléchit à la surface du matériau, et la mesure des variations de température de surface permet de déterminer la température atteinte au point de mesure.
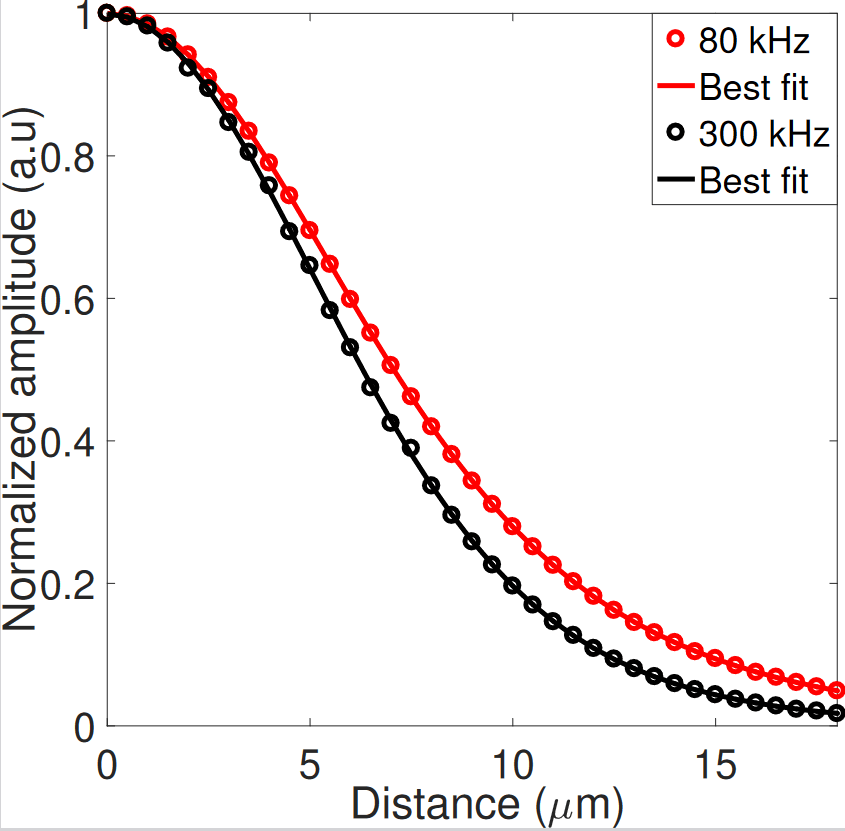
Les domaines d’application sont variés : caractérisation des propriétés thermiques de matériaux en couches minces (conductivité, diffusivité, résistance thermique d’interface), étude de points chauds (défaillance de composants), propriétés thermoélectriques ou électrocaloriques de matériaux.
La vitrification des milieux biologiques est un procédé actuellement fortement étudié, en particulier par les biologistes qui sélectionnent des cryoprotecteurs bio-compatibles. Les études physiques fondamentales concernant la vitrification sont peu nombreuses, alors même que les processus mis en jeu dans ce procédé sont de type physico-chimique. Ces études physiques systématiques sont d’autant plus nécessaires que la vitrification conduit depuis peu à des résultats spectaculaires sur des organes complexes. Il s’agit par exemple de la préservation d’apex de vanille ou de Shih suivie de leur mise en culture, d’ovocytes de brebis, de tissu ovarien, de segments carotidiens, de cellules de racines, ou encore de reins de lapins réimplantés avec succès.Ce projet s’inscrit dans le cadre du développement d’une nouvelle thématique à l’UDSMM. Il s’agit d’étudier à l’aide de techniques photothermiques l’évolution des propriétés thermiques de mélanges cryoprotecteurs lors du refroidissement sur une plage de températures allant de l’ambiant à la température de l’azote liquide.
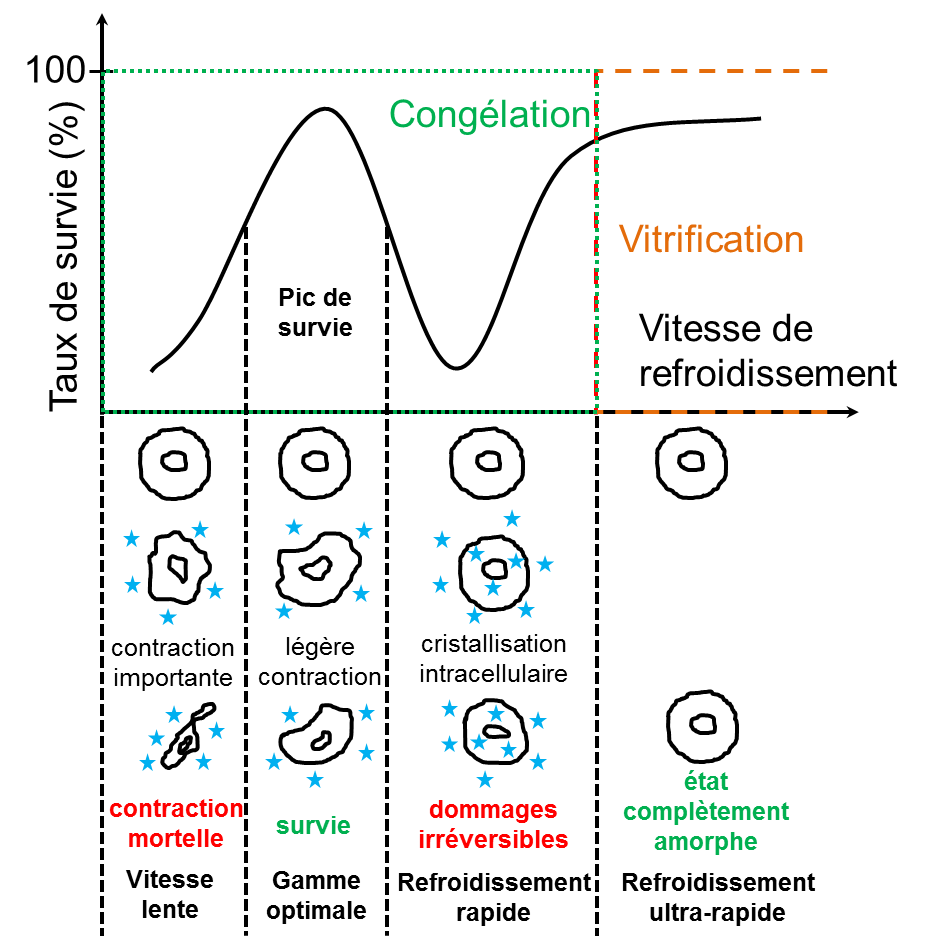
D’après Courbière et al. Gynécologie Obstétrique & Fertilité 37 ( 2009) 803-813
COLLABORATIONS
Collaborations Nationales
Collaborations Internationales
- Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (Belgique).
- Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón (CSIC-Universidad de Zaragoza), (Spain).
- Andrés Sotelo Mieg, National Institute for Isotopic and Molecular Technology de l’Université de Cluj-Napoca, (Roumanie).
- Technical University Asachi of Iasi (Roumanie).
- Université Hassan II de Mohammedia (Maroc).
- Université Libanaise.
- CNRSL (Liban).
PUBLICATIONS
En deux catégories:
_***_
- ACHKAR M., FASQUELLE D., DUPONCHEL B., POUPIN C., HADJ SAHRAOUI A., LONGUEMART S. (2024-04-15). Electrocaloric characterization of samarium doped barium titanate ceramics synthesized by sol-gel process. Ceramics International, 50 (8), 13794-13801,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.01.294
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04433632
- SHISODIA S., SAHRAOUI A. H., DUPONCHEL B., SINGH D. P., DEPRIESTER M. (2024). Optimization of thermoelectric parameters for quantum dot-assisted polymer nanocomposite. Energy Advances, 3 (5), 1037-1046,
http://doi.org/10.1039/D4YA00012A
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04589612
- WANG S., ZHU W., JACOBS I., WOOD W., WANG Z., MANIKANDAN S., ANDREASEN J., UN H., URSEL S., PERALTA S., GUAN S., GRIVEL J., LONGUEMART S., SIRRINGHAUS H. (2024-04-10). Enhancing the Thermoelectric Properties of Conjugated Polymers by Suppressing Dopant‐Induced Disorder. Advanced Materials, , 1-11 / 2314062,
http://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202314062
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04546786
- FARHAT L., BARDOUX M., LONGUEMART S., DUPONCHEL B., HERRO Z., HADJ SAHRAOUI A. (2023-05-06). Measurement of the dynamic temperature response of electrocaloric effect in solid ferroelectric materials via thermoreflectance. Phase Transitions, , 1-9,
http://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2023.2206028
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04458054
- SCHOBING J., MEYER A., LEYSSENS G., ZOUAOUI N., ALLGAIER O., CAZIER F., DEWAELE D., GENEVRAY P., PUSCA C., GOUTIER F. (2023-03). Inventory of the French densified log market: Characterization and emission factors measurement of twenty commercial briquettes. Fuel, 335, 127060,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.127060
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04541003
- ZAIDI M., BAILLIS D., NAOUAR N., DELATTRE F., DEPRIESTER M. (2023-09-20). Thermal Conductivity and Microstructure of Novel Flaxseed-Gum-Filled Epoxy Resin Biocomposite: Analytical Models and X-ray Computed Tomography. Materials, 16 (18), 6318,
http://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186318
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04213221
- CHRISTOPOULOS S., ANGASTINIOTIS N., LAUX – LE GUYON V., BSAIBESS E., KOUTSOKERAS L., DUPONCHEL B., EL-RIFAI J., LI L., SLIMANI A. (2022). Comparative Study of Polyethylene Films Embedded with Oxide Nanoparticles of Granulated and Free-Standing Nature. Polymers, 14 (13), 2629,
http://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132629
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03955377
- BELLAFKIH S., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A., KULINSKI P., DUMOULIN P., LONGUEMART S. (2022-06). Electrocaloric Cooling Prototype Using Lead-Free Barium Titanate Multilayer Capacitors and Heat Transfer Fluid Motion. Journal of Thermal Science and Engineering Applications, 14 (6), 061011,
http://doi.org/10.1115/1.4052896
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04458037
- SHISODIA S., DUPONCHEL B., LEROY G., HADJ SAHRAOUI A., SINGH D. P., POUPIN C., TIDAHY L., COUSIN R., ROPA P., DEPRIESTER M. (2022). Synthesis of quantum dot-based polymer nanocomposites: assessment of their thermoelectric performances. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 6 (13), 3158-3168,
http://doi.org/10.1039/d2se00403h
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04457048
- BSAIBESS E., SAHRAOUI A. H., GLORIEUX C., LEYS J., THOEN J., LONGUEMART S. (2022). Investigation of the electrocaloric effect in BaTiO3 multilayers by pASC calorimetry. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 147 (7), 4837-4843,
http://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10881-5
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04017305
- RADOUANE N., DEPRIESTER M., MAAROUFI A., SINGH D. P., OUAKI B., DUPONCHEL B., ELASS A., TIDAHY L., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A. (2021-08). Synthesis, mechanical, thermal, and electrical characterization of graphite–epoxy composites. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 68 (8), 1456-1465,
http://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.202000490
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04458015
- RADOUANE N., DEPRIESTER M., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A., OUAKI B., ESCORNE B., SINGH D. P., MAAROUFI A. (2021-04-21). Thermoelectric improvement of the figure of merit of zinc phosphate glass composites by a likely tunnel percolation mechanism. Journal of Applied Physics, 129 (15), 155110,
http://doi.org/10.1063/5.0038630
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04456862
- RADOUANE N., HAMMI M., MAAROUFI A., OUAKI B., DEPRIESTER M., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A. (2021-03-01). Investigation on Wettability and Mechanical Properties of Novel Zinc Phosphate Glass-Based Epoxy Composites. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 690 (1), 012047,
http://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/690/1/012047
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04457978
- EL ACHKAR T., MOURA L., MOUFAWAD T., RUELLAN S., PANDA S., LONGUEMART S., LEGRAND F.-X., COSTA GOMES M., LANDY D., GREIGE-GERGES H., FOURMENTIN S. (2020-06). New generation of supramolecular mixtures: Characterization and solubilization studies. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 584, 119443,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119443
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03102809
- RADOUANE N., MAAROUFI A., OUAKI B., POUPIN C., COUSIN R., DUPONCHEL B., SINGH D. P., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A., DEPRIESTER M. (2020-05-15). Thermal, electrical and structural characterization of zinc phosphate glass matrix loaded with different volume fractions of the graphite particles. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 536, 119989,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.119989
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04455818
- SINGH D.P., MISRA A.K., ACHALKUMAR A.S., YELAMAGGAD C.V., DEPRIESTER M. (2019-06-30). Transmuting the blue fluorescence of hekates mesogens derived from tris(N-salicylideneaniline)s core via ZnS/ZnS:Mn2+ semiconductor quantum dots dispersion. Journal of Luminescence, 210, 7 – 13,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.02.009
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03486030
- BADINE E., BARDOUX M., ABBOUD N., DEPRIESTER M., LONGUEMART S., HERRO Z., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A. (2019-05-15). Thermoreflectance profile analysis and multiparameter 3D fitting model applied to the measurement of thermal parameters of thin film materials. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 52 (20), 205303,
http://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ab0ac7
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04457819
- SINGH D.P., MISRA A.K., ACHALKUMAR A.S., YELAMAGGAD C.V., DEPRIESTER M. (2019-06). Transmuting the blue fluorescence of hekates mesogens derived from tris(N-salicylideneaniline)s core via ZnS/ZnS:Mn2+ semiconductor quantum dots dispersion. Journal of Luminescence, 210, 7-13,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.02.009
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04588090
- PRATAP SINGH D., AGRAHARI K., ACHALKUMAR A.S., YELAMAGGAD C.V., MANOHAR R., DEPRIESTER M. (2019-01). Preparation and photophysical properties of soft-nano composites comprising guest anatase TiO 2 nanoparticle and host hekates mesogens. Journal of Luminescence, 205, 304-309,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.09.035
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04455651
- STREZA M., GRAD O., LAZAR D., DEPRIESTER M., LONGUEMART S., SAHRAOUI A.H., BLANITA G., LUPU D. (2019-11). Hybrid MOFs-graphene composites: Correlation between thermal transport and kinetics of hydrogen adsorption. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 143, 118539,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118539
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04457916
- MATHEW A., GOUTIER F., ESCORNE B., ELASS A., LOUIS G., HADJ SAHRAOUI A., BAUDOT A. (2019-06-30). Determination of glass transition temperature using temperature dependent signal from a cryogenic photopyroelectric instrument. Thermochimica Acta, 676, 7 – 12,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.03.027
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03485873
- BSAIBESS E., LOUNES – HADJ SAHRAOUI A., SOUEIDAN M., DUPONCHEL B., SINGH D. P., DAOUDI A., LONGUEMART S. (2019). Study of the electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric liquid crystals. Liquid Crystals, 46 (10), 1517-1526,
http://doi.org/10.1080/02678292.2019.1579928
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04455730
- VENKATACHALAM S., LENFANT S., DEPRIESTER M., SAHRAOUI A. H., HOURLIER D. (2019-12-01). Heat treatment of commercial polydimethylsiloxane PDMS precursors: Part II. Thermal properties of carbon-based ceramic nanocomposites. Ceramics International, 45 (17), 21505-21511,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.07.143
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02369348
- SOTELO A., DEPRIESTER M., TORRES M.A., HADJ-SAHRAOUI A., MADRE M.A., DIEZ J.C. (2018-08). Effect of simultaneous K, and Yb substitution for Ca on the microstructural and thermoelectric characteristics of CaMnO3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 44 (11), 12697-12701,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.071
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04457742
- TORRES M.A., COSTA F.M., FLAHAUT D., TOUATI K., RASEKH S., FERREIRA N.M., ALLOUCHE J., DEPRIESTER M., MADRE M.A., KOVALEVSKY A.V., DIEZ J., SOTELO A. (2018-12). Significant enhancement of the thermoelectric performance in Ca3Co4O9 thermoelectric materials through combined strontium substitution and hot-pressing process. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 39 (4), 1186-1192,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.12.049
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01974115
- DEPRIESTER M., TOUATI K., HADJ SAHRAOUI A. (2018-07-25). Theory of the photothermally generated Seebeck voltage in harmonic regime. EPL – Europhysics Letters, 122 (6), 67001,
http://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/122/67001
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03198401
- BEN AMEUR S., BEL HADJLTAIEF H., BARHOUMI A., DUPONCHEL B., LEROY G., AMLOUK M., GUERMAZI H. (2018-09). Physical investigations and photocatalytic activities on ZnO and SnO2 thin films deposited on flexible polymer substrate. Vacuum, 155, 546-552,
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.05.051
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04465328
- SINGH D. P., BOUSSOUALEM Y., DUPONCHEL B., SAHRAOUI A. H., KUMAR S., MANOHAR R., DAOUDI A. (2018-11-21). Corrigendum: Pico-ampere current sensitivity and CdSe quantum dots assembly assisted charge transport in ferroelectric liquid crystal (2017 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys . 50 325301). Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 51 (46), 469501,
http://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aae2a2
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04455421
- KONDRATENKO K., BOUSSOUALEM Y., LONGUEMART S., DAOUDI A. (2018-10-07). Ionic transport in nematic liquid crystals and alignment layer effects on electrode polarization. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 149 (13), 134902,
http://doi.org/10.1063/1.5045268
https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-04581192
_***_
Eliane BSAIBESS, S Longuemart, Maher SOUEIDAN, Bilal Nsouli, and Abdelak Hadj Sahraoui. A photopyroelectric approach for electrocaloric effect characterization of polar materials. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 51(2):025306, 2017.
Srisaran Venkatachalam, M Depriester, A Hadj Sahraoui, Bruno Capoen, MR Ammar, and D Hourlier. Thermal conductivity of kapton-derived car- bon. Carbon, 114:134–140, 2017.
K Touati, M Depriester, E Guilmeau, Andres Sotelo, A Maignan, MA Madre, Franck Gascoin, and AH Sahraoui. Generalized theory of the self-induced voltage by seebeck effect in frequency domain. 2017.
Karim Touati, Michael Depriester, Emmanuel Guilmeau, Andr´es Sotelo, Maria A Madre, Franck Gascoin, and Abdelhak Hadj Sahraoui. General approach of the photothermoelectric technique for thermal characterization of solid thermoelectric materials. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 50(26):265501, 2017.
C Tripon, M Depriester, I Craciunescu, D Dadarlat, AH Sahraoui, et al. Photothermoelectric detection of phase transitions in liquid ther- moelectrics. Journal of Advanced Thermal Science Research, 4:1–4, 2017.
DP Singh, V Kumar, A Kumar, R Manohar, Renu Pasricha, B Duponchel, Y Boussoualem, AH Sahraoui, and A Daoudi. Effect of graphene oxide interlayer electron-phonon coupling on the electro-optical parameters of a ferroelectric liquid crystal. RSC advances, 7(21):12479–12485, 2017.
A. Mathew, B. Escorne, A. Elass, F. Goutier, A. Baudot, G. Louis, A. Hadj Sahraoui,Low temperature photo pyroelectric study on the glassy state in the presence of cryoprotectants – comparison with DSC and viscosity studies, Cryogenics 2017. Proceedings of the 14th IIR International Conference: Dresden 2017 : doi.org/10.18462/iir.cryo.2017.0038
E. Bsaibess, S. Longuemart, M. Soueidan, B. Nsouli, A. Hadj Sahraoui, A photopyroelectric approach for electrocaloric effect characterization of polar materials. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 51(2), 025306, 2017, doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa9dfb
Touati, K., Depriester, M., Guilmeau, E., Sotelo, A., Sediles, M. M., Gascoin, F., & Hadj Sahraoui, A. . General approach of the photothermoelectric technique for thermal characterization of solid thermoelectric materials. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 50 265501 ,2017. doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/aa748d
Michal Pawlak, Mihaela Streza, Cristian Morari, Karol Strzałkowski, Michael Depriester and Mihai Chirtoc
Quantitative thermal wave phase imaging of an IR semi-transparent GaAs wafer using IR lock-in thermography, Meas. Sci. Technol. 28 025008, 2017 doi:10.1088/1361-6501/aa4f69
S. Venkatachalam, M. Depriester, A. Hadj Sahraoui, B. Capoen, M.R. Ammar, D. Hourlier, Thermal conductivity of Kapton-derived carbon, Carbon, Volume 114,134-140, 2017 doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2016.11.072.
M.A. Madre, Sh. Rasekh, K. Touati, C. Salvador, M. Depriester, M.A. Torres, P. Bosque, J.C. Diez, A. Sotelo, From nanosized precursors to high performance ceramics: The case of Bi2Ca2Co1.7Ox, Materials Letters, Volume 191, 14-16, 2017, doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2017.01.031.
K. Touati, M. Depriester, A. Hadj Sahraoui, C. Tripon, D. Dadarlat, Combined photopyroelectric-photothermoelectric detection for thermal characterization of liquid thermoelectrics, Thermochimica Acta, 642, 20, 39-44, 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2016.09.004.
Jan Leys, Christ Glorieux and Jan Thoen Temperature Dependence of Enthalpy and Heat Capacity of Alkanes and Related Phase Change Materials (PCMs) with a Peltier-element-based Adiabatic Scanning Calorimeter. MRS Advances, Available on CJO 2016 doi:10.1557/adv.2016.298
Streza M; Longuemart S.; Guilmeau E.; Strzalkowski K.; Touati K., Depriester M, Maignan A.;Hadj Sahraoui A., An active thermography approach for thermal and electrical characterization of thermoelectric materials, J. Phys. D : Appl. Phys., 49, 285601, 2016. DOI : 10.1088/0022-3727/49/28/285601
Leys Jan; Duponchel Benoît; Longuemart Stéphane; Glorieux Christ; Thoen Jan; A new calorimetric technique for phase change materials and its application to alkane-based PCMs, Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 5, 2016 :DOI: 10.1007/s40243-016-0068-y
Dadarlat, E. Guilmeau, A. Hadj Sahraoui, C. Tudoran, V. Surducan, C. Bourgès, P. Lemoine, Photothermoelectric (PTE) Versus Photopyroelectric (PPE) Detection of Phase Transitions, International Journal of Thermophysics 37 (5), 53, 2016
Touati Karim; Depriester Michael; Kuriakose Maju; Hadj Sahraoui Abdelhak, New methodology for the thermal characterization of thermoelectric liquids, Review of Scientific Instruments, 86, 9, 094901, 2015: DOI :10.1063/1.4930125
Dadarlat Dorin; Misse Patrick RN; Maignan Antoine; Guilmeau Emmanuel; Turcu Rodica; Vekas Ladislau; Tudoran Cristian; Depriester Michael; Hadj Sahraoui Abdelhak, Alternative Calorimetry Based on the Photothermoelectric (PTE) Effect: Application to Magnetic, Nanofluids, International Journal of Thermophysics, 1-11, 2015.
Dadarlat, D; Misse, PRN; Maignan, A; Guilmeau, E; Depriester, M; Kuriakose, M; Sahraoui, A Hadj; Thermoelectrics (TE) used as detectors of radiation: an alternative calorimetry based on the photothermoelectric (PTE) effect, Advanced Topics in Optoelectronics, Microelectronics, and Nanotechnologies, 92582R-10, 2015.
Roussel, Frederick; King, Roch Chen Yu; Kuriakose, Maju; Depriester, Mickael; Hadj-Sahraoui, Abdelhak; Gors, Carole; Addad, Ahmed; Brun, Jean-Francois, Electrical and thermal transport properties of polyaniline/silver composites and their use as thermoelectric materials, Synthetic Metals, 199, 196-204, 2015.
Islam Rakibul; Chan-Yu-King Roch; Brun Jean-François; Gors Carole; Addad Ahmed; Depriester, Michael; Hadj-Sahraoui Abdelhak; Roussel Frederick, Transport and thermoelectric properties of polyaniline/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites, Nanotechnology, 25, 47, 475705, 2014.
Leys, J., Tripathi, C. S. P., Glorieux, C., Zahn, S., Kirchner, B., Longuemart, S & Binnemans, K. (2014). Electrical conductivity and glass formation in nitrile-functionalized pyrrolidinium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide ionic liquids: chain length and odd–even effects of the alkyl spacer between the pyrrolidinium ring and the nitrile group, Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,16, 22, 10548-10557, 2014
Kuriakose, Maju; Depriester, Michael; King, Roch Chan Yu; Roussel, Frédérick; Abdelhak, Hadj Sahraoui, Use of Photothermally Generated Seebeck Voltage for Thermal Characterization of Thermoelectric Materials,Journal of Electronic Materials, 43, 6, 1740-1743, 2014.
Kuriakose, M; Longuemart, S; Depriester, M; Delenclos, S; Hadj Sahraoui, Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars effects on the thermal-transport properties of polymer-dispersed liquid crystals, Physical Review E, 89, 2, 022511,2014.
Dadarlat, D; Streza, M; King, R Chan Yu; Roussel, F; Kuriakose, M; Depriester, M; Guilmeau, E; Sahraoui, A Hadj; , »The photothermoelectric technique (PTE), an alternative photothermal calorimetry »,Measurement Science and Technology, 25, 1, 015603, 2014.
S. Hany, B. Duponchel, C. Poupin, A. Aboukaïs, D. Dewaele, J-B. Vogt, J. Bouquerel, H. Kassem, A. Mouftiez, S. Hariri, M. Milochova, E.Bychkov, E. Abi-Aad, Microstructural and mechanical properties of 9%Ni steels used for the construction of LNG storage tanks. Adv. Mat. Res. 936, 1953-1957, 2014
D. Dadarlat, M. N. Pop, O. Onija, M. Streza, M. M. Pop, S. Longuemart, M. Depriester, A. Hadj Sahraoui, V. Simon, Photopyroelectric (PPE) calorimetry of composite materials, Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 111 (2) 2, pp 1129-1132 2013.
M. Kuriakose, M. Depriester, R. Chan Yu King, F. Roussel, A. Hadj Sahraoui, Photothermoelectric effect as a means for thermal characterization of nanocomposites based on intrinsically conducting polymers and carbon nanotubes J. Appl. Phys. 113, 044502,2013.
M. Streza, D. Dadarlat, Y. Fedala, S. Longuemart, Depth estimation of surface cracks on metallic components by means of lock-in thermography, Review of Scientific Instruments, 84 (7), 074902 ,2013
M. Kuriakose, M. Depriester, D. Dadarlat, A. Hadj Sahraoui, Improved methods for measuring thermal parameters of liquid samples using photothermal infrared radiometry, Measurement Science and Technology. 24, 025603, 2013
A. Boulerouah, S. Longuemart, P. Hus, A. Hadj Sahraoui, Ethanol-sensing properties of potassium bromide/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites, Journal of Materials Science, 48 (22), 8023-8028, 2013
F. Lebel, E. Abi-Aad, B. Duponchel, I. Proriol-Serre, S. Ringot, P. Langry, A. Aboukais, Thermal ageing process at laboratory scale to evaluate the lifetime of Liquefied Natural Gas storage and loading/unloading materials, Materials & Design 44, 283-290, 2013
M. Kuriakose, M. Depriester, M. Mascot, S. Longuemart, D. Fasquelle, J.C. Carru, A. Hadj Sahraoui, Thermal parameter extraction of a multilayered system by a genetic algorithm, International Journal of Thermophysics, 34 (8-9), 1569-1578,2, 2013

